Claiming a brand or commodity is green without any supporting evidence

No Proof
Making baseless claims is one of the easiest greenwashing tactics. For example when an advertisement claims that a product has several environmental benefits, but the company can’t back up these claims with any scientific data or evidence.
Share this insight on Twitter…
Greenwashing Tactic #2: No Proof: Claiming a #brand or #commodity is sustainable without any evidence. We’ve had enough of #greenwashing lies to sell so-called ‘sustainable’ #palmoil #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife
Tweet
The RSPO promises to deliver this with their certification:
1. Improves the livelihoods of small holder farmers
2. Stops illegal indigenous land-grabbing and human rights abuses
3. Stops deforestation
They sell the idea of ‘sustainable’ palm oil to consumers so that they will continue to buy it from brands using it.

Greenwashing with No Proof
The reassurances of certified sustainable palm oil are based on promises, not real world outcomes.
Consumers are offered the reassuring lie of sustainable palm oil with little proof or evidence that it actually works.
The Roundtable for Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) ads
Each of these claims by the Roundtable of Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) are not supported by OSINT and peer-reviewed research, by investigative reports from journalists or environmental and human rights NGOs. These are examples of ‘Greenwashing with No Proof’.

Malaysian Palm Oil Council: ‘Tree of Life’ ad
In this TVC, the Malaysian Palm Oil Council called the destructive crop ‘The Tree of Life that helps our planet to breathe, and gives a home to hundreds of species of flora and fauna’.
Much to the council’s embarrassment, the TV advertisement, along with the amended version from the following year were both banned by the British Advertising Standards Authority because they were deemed misleading.
Read more: Greenwash and spin: palm oil lobby targets its critics, The Ecologist.
Reality:
The sustainability standards of the RSPO haven’t managed to stop deforestation, human rights abuses, violence, illegal indigenous land-grabbing and endangered species protection.
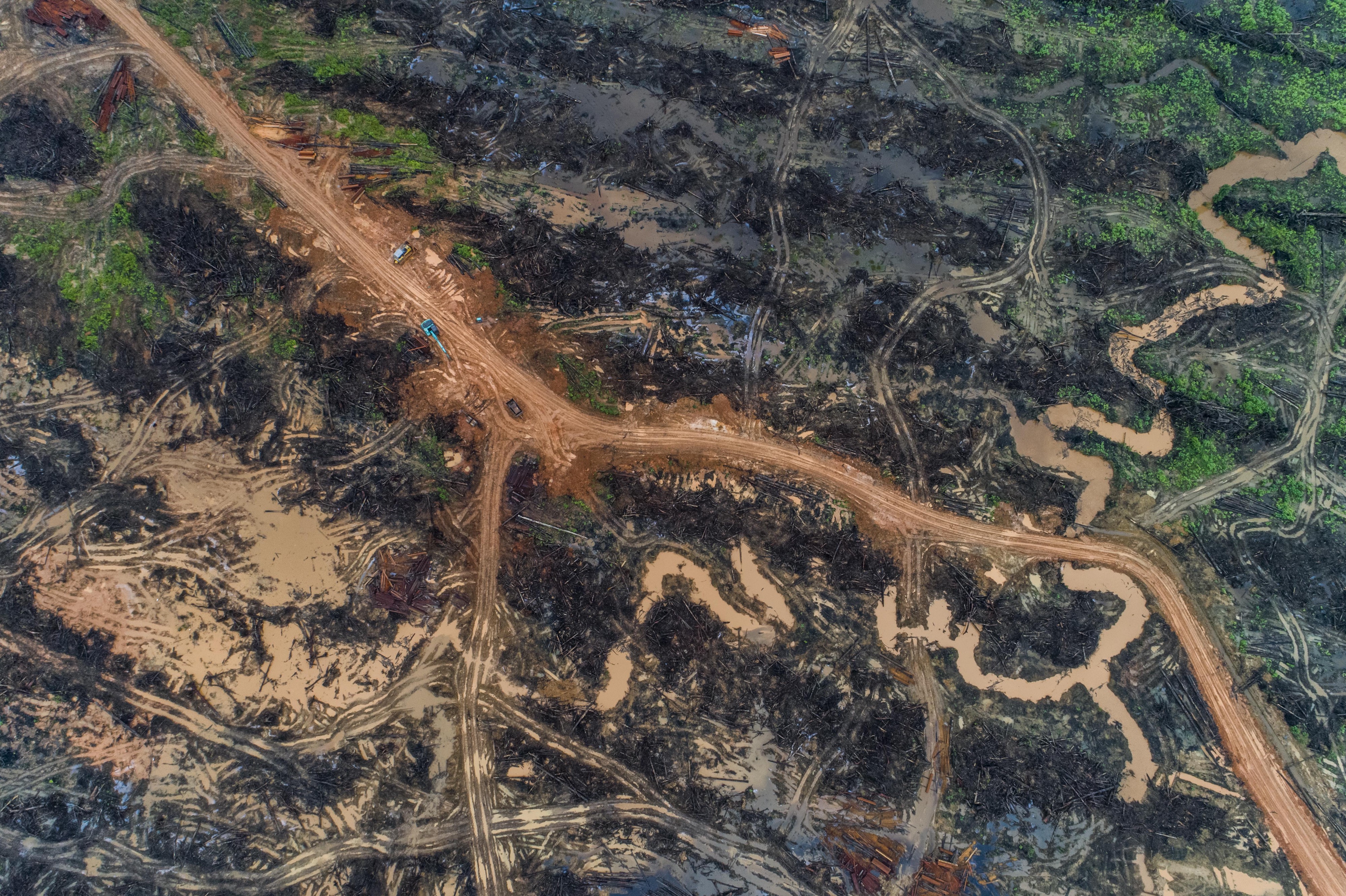

RSPO: 14 years of failure to eliminate violence and destruction from the industrial palm oil sector
Friends of the Earth and 100 other human rights and environmental NGOS co-signed this letter in 2018
Letter
During its 14 years of existence, RSPO – the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil – has failed to live up to its claim of “transforming” the industrial palm oil production sector into a so-called “sustainable” one. In reality, the RSPO has been used by the palm oil industry to greenwash corporate destruction and human rights abuses, while it continues to expand business, forest destruction and profits.
RSPO presents itself to the public with the slogan “transforming the markets to make sustainable palm oil the norm”. Palm oil has become the cheapest vegetable oil available on the global market, making it a popular choice among the group that dominates RSPO membership, big palm oil buyers.
They will do everything to secure a steady flow of cheap palm oil. They also know that the key to the corporate success story of producing “cheap” palm oil is a particular model of industrial production, with ever-increasing efficiency and productivity which in turn is achieved by:
- Planting on a large-scale and in monoculture, frequently through conversion of tropical biodiverse forests
- Using “high yielding” seedlings that demand large amounts of agrotoxics and abundant water.
- Squeezing cheap labour out of the smallest possible work force, employed in precarious conditions so that company costs are cut to a minimum
- Making significant up-front money from the tropical timber extracted from concessions, which is then used to finance plantation development or increase corporate profits.
- Grabbing land violently from local communities or by means of other arrangements with governments (including favourable tax regimes) to access land at the lowest possible cost.
Those living on the fertile land that the corporations choose to apply their industrial palm oil production model, pay a very high price.
Violence is intrinsic to this model:
- violence and repression when communities resist the corporate take over of their land because they know that once their land is turned into monoculture oil palm plantations, their livelihoods will be destroyed, their land and forests invaded. In countless cases, deforestation caused by the expansion of this industry, has displaced communities or destroyed community livelihoods where
- companies violate customary rights and take control of community land;
- sexual violence and harassment against women in and around the plantations which often stays invisible because women find themselves without possibilities to demand that the perpetrators be prosecuted;
- Child labour and precarious working conditions that go hand-in-hand with violation of workers’ rights;
- working conditions can even be so bad as to amount to contemporary forms of slavery. This exploitative model of work grants companies more economic profits while allowing palm oil to remain a cheap product. That is why, neither them or their shareholders do anything to stop it.
- exposure of workers, entire communities and forests, rivers, water springs, agricultural land and soils to the excessive application of agrotoxics;
- depriving communities surrounded by industrial oil palm plantations of their food sovereignty when industrial oil palm plantations occupy land that communities need to grow food crops.
RSPO’s proclaimed vision of transforming the industrial oil palm sector is doomed to fail because the Roundtable’s certification principles promote this structural violent and destructive model.
The RSPO also fails to address the industry’s reliance on exclusive control of large and contingent areas of fertile land, as well as the industry’s growth paradigm which demands a continued expansion of corporate control over community land and violent land grabs.
None of RPSO’s eight certification principles suggests transforming this industry reliance on exclusive control over vast areas of land or the growth paradigm inherent to the model.
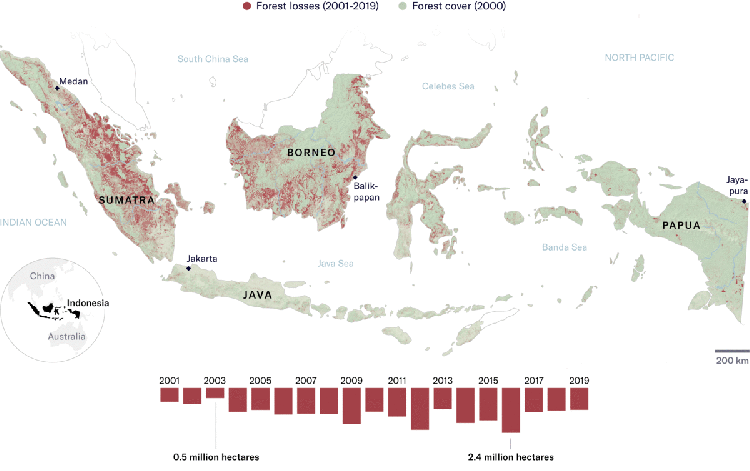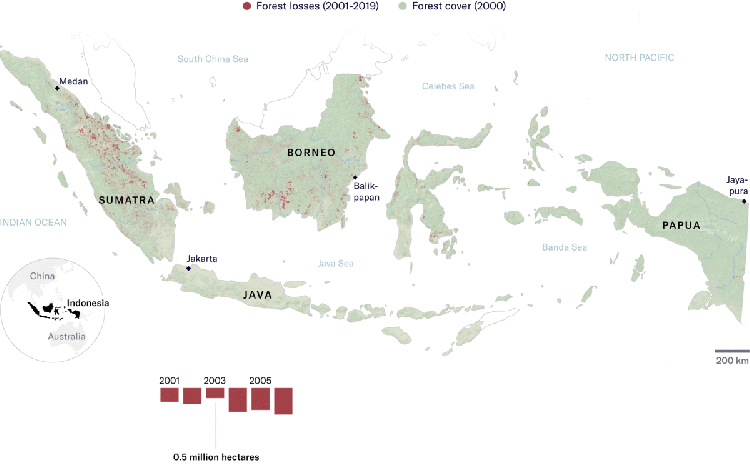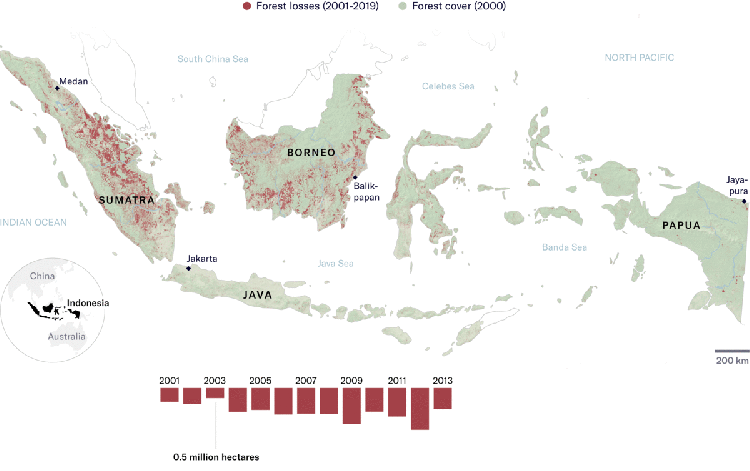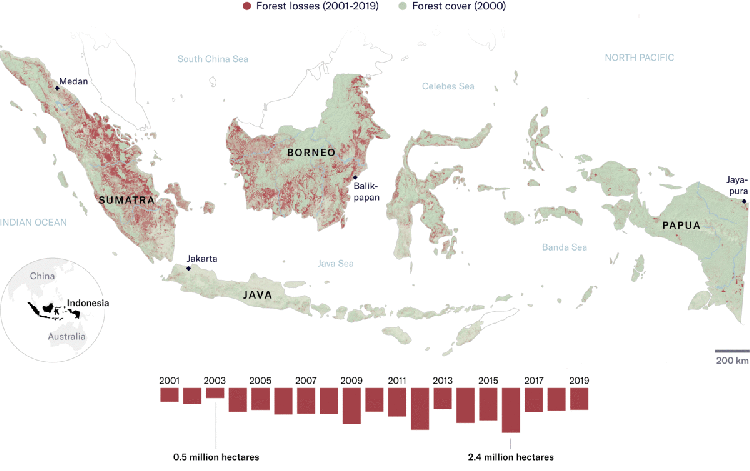
Industrial use of vegetable oils has doubled in the past 15 years, with palm oil being the cheapest. This massive increase of palm oil use in part explains the current expansion of industrial oil palm plantations, especially in Africa and Latin America, from the year 2000 onward, in addition to the existing vast plantations areas in Malaysia and Indonesia that also continue expanding.
On the ground, countless examples show that industrial oil palm plantations continue to be synonymous to violence and destruction for communities and forests. Communities’ experiences in the new industrial oil palm plantation frontiers, such as Gabon, Nigeria, Cameroon, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Peru, Honduras, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, are similar to past and ongoing community experiences in Indonesia and Malaysia.
RSPO creates a smokescreen that makes this violence invisible for consumers and financiers. Governments often fail to take regulatory action to stop the expansion of plantations and increasing demand of palm oil; they rely on RSPO to deliver an apparently sustainable flow of palm oil.
For example, in its public propaganda, RSPO claims it supports more than 100,000 small holders. But the profit from palm oil production is still disproportionally appropriated by the oil palm companies: in 2016, 88% of all certified palm oil came from corporate plantations and 99,6% of the production is corporate-controlled.
RSPO also claims that the principle of Free, Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC) is key among its own Principles and Criteria. The right to FPIC implies, among others, that if a community denies the establishment of this monoculture in its territory, operations cannot be carried out. Reality shows us, however, that despite this, many projects go ahead.
Concessions are often guaranteed long before the company reaches out to the affected communities. Under these circumstances, to say that FPIC is central to RSPO is bluntly false and disrespectful.
RSPO also argues that where conflicts with the plantation companies arise, communities can always use its complaint mechanism. However, the mechanism is complex and it rarely solves the problems that communities face and want to resolve.
This becomes particularly apparent in relation to land legacy conflicts where the mechanism is biased against communities. It allows companies to continue exploiting community land until courts have come to a decision. This approach encourages companies to sit out such conflicts and count on court proceedings dragging on, often over decades.
Another argument used by RSPO is that industrial oil palm plantations have lifted millions of people out of poverty. That claim is certainly questionable, even more so considering that there is also an important number of people who have been displaced over the past decades to make space for plantations.
Indigenous communities have in fact lost their fertile land, forests and rivers to oil palm plantations, adversely affecting their food, culture and local economies.
The RSPO promise of “transformation” has turned into a powerful greenwashing tool for corporations in the palm oil industry. RSPO grants this industry, which remains responsible for violent land grabbing, environmental destruction, pollution through excessive use of agrotoxics and destruction of peasant and indigenous livelihoods, a “sustainable” image.
What’s more, RSPO membership seems to suffice for investors and companies to be able to claim that they are “responsible” actors. This greenwash is particularly stunning, since being a member does not guarantee much change on the ground. Only recently, a company became RSPO member after it was found to deforest over 27.000 hectares of rainforest in Papua, Indonesia.
Certification is structurally dependent on the very same policies and regulation that have given rise to the host of environmental devastation and community land rights violations associated with oil palm plantations. These systemic governance issues are part of the destructive economic model, and embedded in state power.
For this reason, voluntary certification schemes cannot provide adequate protection for forests, community rights, food sovereignty and guarantee sustainability. Governments and financiers need to take responsibility to stop the destructive palm oil expansion that violates the rights of local communities and Indigenous Peoples.
As immediate steps, governments need to:
- Put in place a moratorium on palm oil plantations expansion and use that as a breathing space to fix the policy frameworks;
- Drastically reduce demand for palm oil: stop using food for fuel;
- Strengthen and respect the rights of local communities and Indigenous Peoples to amongst others, self-determination and territorial control.
- Promote agro-ecology and community control of their forests, which strengthens local incomes, livelihoods and food sovereignty, instead of advancing industrial agro-businesses.
Signatures
- Aalamaram-NGOAcción Ecológica, Ecuador
- ActionAid, France
- AGAPAN
Amics arbres - Arbres amics
- Amis de la Terre France
- ARAARBA (Asociación para la Recuperación del Bosque Autóctono)
- Asociación Conservacionista YISKI, Costa Rica
Asociación Gaia El Salvador - Association Congo Actif, Paris
- Association Les Gens du Partage, Carrières-sous-Poissy
- Association pour le développement des aires protégées, Swizterland
- BASE IS
- Bézu St Eloi
- Boxberg OT Uhyst
- Bread for all
- Bruno Manser Fund
- CADDECAE, Ecuador
- Campaign to STOP GE Trees
- CAP, Center for Advocacy Practices
- Centar za životnu sredinu/ Friends of the Earth Bosnia and Herzegovina
- CESTA – FOE El Salvador
- CETRI – Centre tricontinental
- Climate Change Kenya
- Coalición de Tendencia Clasista. (CTC-VZLA)
- Colectivo de Investigación y Acompañmiento Comunitario
- Collectif pour la défense des terres malgaches – TANY, Madagascar
- Community Forest Watch, Nigeria
- Consumers Association of Penang
- Corporate Europe Observatory
- Cuttington University
- Down to Earth Consult
- El Campello
- Environmental Resources Management and Social Issue Centre (ERMSIC) Cameroon
- Environmental Rights Action/Friends of the Earth Nigeria
- FASE ES , Brazil
- Fédération romande des consommateurs
- FENEV, (Femmes Environnement nature Entrepreneuriat Vert).
- Focus on the Global South
- Forum Ökologie & Papier, Germany
- Friends of the Earth Ghana
- Friends of the Earth International
- GE Free NZ, New Zealand
- Global Alliance against REDD
- Global Justice Ecology Project
- Global Info
- Gobierno Territorial Autónomo de la Nación Wampís , Peru
- GRAIN
- Green Development Advocates (GDA)
- CameroonGreystones, Ireland
- Groupe International de Travail pour les Peuples Autochtones
Grupo ETC - Grupo Guayubira, Uruguay
- Instituto Mexicano de Gobernanza Medioambiental AC Instituto Mexicano de Gobernanza Medioambiental AC
- Integrated Program for the Development of the Pygmy People (PIDP), DRC
- Justica Ambiental
- Justicia Paz e Integridad de la Creacion. Costa Rica
- Kempityari
- Latin Ambiente, http://www.latinambiente.org
- Les gens du partage
- LOYOLA SCHOOL OF THEOLOGY, MANILA
- Maderas del Pueblo del Sureste, AC
- Maiouri nature, Guyane
- Mangrove Action Project
- Milieudefensie – Friends of the Earth Netherlands
- Movimento Amigos da Rua Gonçalo de Carvalho
- Muyissi Environnement, Gabon
- Nature-d-congo de la République du Congo
- New Wind Association from Finland
- NOAH-Friends of the Earth Denmark
- Oakland Institute
- OFRANEH, Honduras
- Ole Siosiomaga Society Incorporated (OLSSI)
- ONG OCEAN : Organisation Congolaise des Ecologistes et Amis de la Nature et sommes basés en RD Congo.
- OPIROMA, Brazil
- Otros Mundos A.C./Amigos de la Tierra México
- Paramo Guerrrero Zipaquira
- PROYECTO GRAN SIMIO (GAP/PGS-España)
- Quercus – ANCN, Portugal
- Radd (Reseau des Acteurs du Développement Durable) , Cameroon
- Rainforest Foundation UK
- Rainforest Relief
- ReAct – Alliances Transnationales
- RECOMA – Red latinoamericana contra los monocultivos de árboles
- Red de Coordinacion en Biodiversidad , Çosta Rica
- REFEB-Cote d’Ivoire
- Rettet den Regenwald, Germany
- ROBIN WOOD
- Sahabat Alam Malaysia (Friends of the Earth Malaysia)
- Salva la Selva
- School of Democratic Economics, Indonesia
- Serendipalm Company Limited
- Sherpa , The Netherlands
- SYNAPARCAM, Cameroon
- The Corner House, UK
Towards Equitable Sustainable Holistic Development - TRAFFED KIVU ,RD. CONGOUNIÓN UNIVERSAL DESARROLLO SOLIDARIO
University of Sussex, UK - UTB ColombiaWatch Indonesia!
- WESSA
World Rainforest Movement - Youth Volunteers for the Environment Ghana
“Environmental damage and social injustice were reasons why the global palm oil certification, the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) was established. In practice, requirements for oil palm certifications are easily violated. Lots of things are problematic. Often location permits are issued by the central and local governments and they neglect important social responsibilities to indigenous peoples.
— Dr Setia Budhi, Dayak Ethnographer
Research shows that RSPO certified sustainable palm oil does not:
- Improve farmer livelihoods.
- Provide protection for endangered species.
- Prevent deforestation and fires.
We find that, while sustainability standards can help improve the sustainability of production processes in certain situations, they are insufficient to ensure food system sustainability at scale, nor do they advance equity objectives in agrifood supply chains.
Meemken, EM., Barrett, C.B., Michelson, H.C. et al. Sustainability standards in global agrifood supply chains. Nat Food (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00360-3
There was no significant difference was found between certified and non-certified plantations for any of the sustainability metrics investigated, however positive economic trends including greater fresh fruit bunch yields were revealed. To achieve intended outcomes, RSPO principles and criteria are in need of substantial improvement and rigorous enforcement.
Morgans, C. L. et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of palm oil certification in delivering multiple sustainability objectives. Environ. Res. Lett. 13, 064032 (2018).
Oil palm plantations support much fewer species than do forests and often also fewer than other tree crops. Further negative impacts include habitat fragmentation and pollution, including greenhouse gas emissions.
Brühl, Paul F. Donald, Ben Phalan, How will oil palm expansion affect biodiversity?,
Trends in Ecology & Evolution, Vol 23, 2008, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2008.06.012.
‘Is there such a thing as sustainable palm oil? Satellite images show protected rainforest on fire’
Adina Renner, Conradin Zellweger, Barnaby Skinner, (2021), Neue Zürcher Zeitung.

Join the #Boycott4Wildlife and fight deforestation, greenwashing and animal extinction by using your wallet as a weapon!
Further reading on palm oil ecocide, greenwashing and deceptive marketing
- A Brief History of Consumer Culture, Dr. Kerryn Higgs, The MIT Press Reader. https://thereader.mitpress.mit.edu/a-brief-history-of-consumer-culture/
- A Deluge of Double-Speak (2017), Jason Bagley. Truth in Advertising. https://truthinadvertising.org/blog/a-deluge-of-doublespeak/
- Aggarwal, P. (2011). Greenwashing: The darker side of CSR. Indian Journal of Applied Research, 4(3), 61-66. https://www.worldwidejournals.com/indian-journal-of-applied-research-(IJAR)/article/greenwashing-the-darker-side-of-csr/MzMxMQ==/?is=1
- Anti-Corporate Activism and Collusion: The Contentious Politics of Palm Oil Expansion in Indonesia, (2022). Ward Berenschot, et. al., Geoforum, Volume 131, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2022.03.002
- Armour, C. (2021). Green Clean. Company Director Magazine. https://www.aicd.com.au/regulatory-compliance/regulations/investigation/green-clean.html
- Balanced Growth (2020), In: Leal Filho W., Azul A.M., Brandli L., özuyar P.G., Wall T. (eds) Responsible Consumption and Production. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham
- Berenschot, W., Hospes, O., & Afrizal, A. (2023). Unequal access to justice: An evaluation of RSPO’s capacity to resolve palm oil conflicts in Indonesia. Agriculture and Human Values, 40, 291-304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-022-10360-z
- Carlson, K. M., Heilmayr, R., Gibbs, H. K., Noojipady, P., et al. (2018). Effect of oil palm sustainability certification on deforestation and fire in Indonesia. PNAS, 115(1), 121-126. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1704728114
- Cazzolla Gatti, R., Liang, J., Velichevskaya, A., & Zhou, M. (2018). Sustainable palm oil may not be so sustainable. Science of The Total Environment, 652, 48-51. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30359800/
- Changing Times Media. (2019). Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil is ‘greenwashing’ labelled products, environmental investigation agency says. Changing Times Media. https://changingtimes.media/2019/11/03/roundtable-on-sustainable-palm-oil-is-greenwashing-labelled-products-environmental-protection-agency-says/
- Client Earth: The Greenwashing Files. https://www.clientearth.org/projects/the-greenwashing-files/
- Commodifying sustainability: Development, nature and politics in the palm oil industry (2019). World Development, Volume 121, September 2019, Pages 218-228. https://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/wdevel/v121y2019icp218-228.html
- Contrasting communications of sustainability science in the media coverage of palm oil agriculture on tropical peatlands in Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore (2020). Liu, F. H. M., Ganesan, V., Smith, T. E. L. Environmental Science & Policy, 114. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343772443_Contrasting_communications_of_sustainability_science_in_the_media_coverage_of_palm_oil_agriculture_on_tropical_peatlands_in_Indonesia_Malaysia_and_Singapore
- Cosimo, L. H. E., Masiero, M., Mammadova, A., & Pettenella, D. (2024). Voluntary sustainability standards to cope with the new European Union regulation on deforestation-free products: A gap analysis. Forest Policy and Economics, 164, 103235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2024.103235
- Dalton, J. (2018). No such thing as sustainable palm oil – ‘certified’ can destroy even more wildlife, say scientists. The Independent. https://www.independent.co.uk/climate-change/news/palm-oil-sustainable-certified-plantations-orangutans-indonesia-southeast-asia-greenwashing-purdue-a8674681.html
- Davis, S. J., Alexander, K., Moreno-Cruz, J., et al. (2023). Food without agriculture. Nature Sustainability. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-023-01241-2
- EIA International. (2022). Will palm oil watchdog rid itself of deforestation or continue to pretend its products are sustainable? EIA International. https://eia-international.org/news/will-palm-oil-watchdog-rid-itself-of-deforestation-or-continue-to-pretend-its-products-are-sustainable/
- Environmental Investigation Agency. (2019). Palm oil watchdog’s sustainability guarantee is still a destructive con. EIA International. https://eia-international.org/news/palm-oil-watchdogs-sustainability-guarantee-is-still-a-destructive-con/
- Federal Trade Commission. (n.d.). Green Guides. https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/topics/truth-advertising/green-guides
- Fifteen environmental NGOs demand that sustainable palm oil watchdog does its job (2019). Rainforest Action Network. https://www.ran.org/press-releases/fifteen-environmental-ngos-demand-that-sustainable-palm-oil-watchdog-does-its-job/
- Friends of the Earth International. (2018). RSPO: 14 years of failure to eliminate violence and destruction from the industrial palm oil sector. Friends of the Earth International. https://www.foei.org/rspo-14-years-of-failure-to-eliminate-violence-and-destruction-from-the-industrial-palm-oil-sector/
- Lang, Chris and REDD Monitor. Sustainable palm oil? RSPO’s greenwashing and fraudulent audits exposed. The Ecologist. https://theecologist.org/2015/nov/19/sustainable-palm-oil-rspos-greenwashing-and-fraudulent-audits-exposed
- Gatti, L., Pizzetti, M., & Seele, P. (2021). Green lies and their effect on intention to invest. Journal of Business Research, 127, 376-387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.01.028
- Global Witness. (2023). Amazon palm: Ecocide and human rights abuses. Global Witness. https://www.globalwitness.org/en/campaigns/environmental-activists/amazon-palm/
- Global Witness. (2021). The True Price of Palm Oil. Global Witness. https://www.globalwitness.org/en/campaigns/forests/true-price-palm-oil/
- Grain. (2021). Ten reasons why certification should not be promoted in the EU anti-deforestation regulation. Grain. https://grain.org/en/article/6856-ten-reasons-why-certification-should-not-be-promoted-in-the-eu-anti-deforestation-regulation
- Green Clean (2021). Armour, C. Company Director Magazine.
- Green marketing and the Australian Consumer Law (2011). Australian Competition and Consumer Commission. https://www.accc.gov.au/system/files/Green%20marketing%20and%20the%20ACL.pdf
- Greenwash and spin: palm oil lobby targets its critics (2011). Helan, A. Ecologist: Informed by Nature. https://theecologist.org/2011/jul/08/greenwash-and-spin-palm-oil-lobby-targets-its-critics
- Greenwashing: definition and examples. Selectra https://climate.selectra.com/en/environment/greenwashing#:~:text=Greenwashing%20is%20the%20practice%20of,its%20activities%20pollute%20the%20environment.
- Greenwashing of the Palm Oil Industry (2007). Mongabay. https://news.mongabay.com/2007/11/greenwashing-the-palm-oil-industry/
- Group Challenges Rainforest Alliance Earth-Friendly Seal of Approval (2015). Truth in Advertising. https://www.truthinadvertising.org/group-challenges-rainforest-alliance-earth-friendly-seal-of-approval
- Helan, A. (2011). Greenwash and spin: palm oil lobby targets its critics. Ecologist: Informed by Nature. https://theecologist.org/2011/feb/15/greenwash-and-spin-palm-oil-lobby-targets-its-critics
- Hewlett Packard. (2021). What is Greenwashing and How to Tell Which Companies are Truly Environmentally Responsible. Hewlett Packard. https://www.hp.com/us-en/shop/tech-takes/what-is-greenwashing-environmentally-responsible-companies
- Holzner, A., Rameli, N. I. A. M., Ruppert, N., & Widdig, A. (2024). Agricultural habitat use affects infant survivorship in an endangered macaque species. Current Biology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38194972/
- How Cause-washing Deceives Consumers (2021). Truth in Advertising. https://truthinadvertising.org/resource/how-causewashing-deceives-consumers/
- International Labour Organization. (2020). Forced labor in the palm oil industry. ILO. https://www.ilo.org/topics/forced-labour-modern-slavery-and-human-trafficking
- Jauernig, J., Uhl, M., & Valentinov, V. (2021). The ethics of corporate hypocrisy: An experimental approach. Futures, 129, 102757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.futures.2021.102757
- Kirby, D. (2015). Sustainable Palm Oil? Who Knows, Thanks to Derelict Auditors. Take Part. https://www.yahoo.com/news/sustainable-palm-oil-knows-thanks-derelict-auditors-200643980.html
- Li, T. M., & Semedi, P. (2021). Plantation life: Corporate occupation in Indonesia’s oil palm zone. Duke University Press. https://www.dukeupress.edu/plantation-life
- Liu, F. H. M., Ganesan, V., & Smith, T. E. L. (2020). Contrasting communications of sustainability science in the media coverage of palm oil agriculture on tropical peatlands in Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore. Environmental Science & Policy, 114. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343772443_Contrasting_communications_of_sustainability_science_in_the_media_coverage_of_palm_oil_agriculture_on_tropical_peatlands_in_Indonesia_Malaysia_and_Singapore
- Meemken, E. M., Barrett, C. B., Michelson, H. C., et al. (2021). Sustainability standards in global agrifood supply chains. Nature Food. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-021-00299-2
- Miles, T. (2019). Study in WHO journal likens palm oil lobbying to tobacco and alcohol industries. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSKCN1P21ZR/
- Nygaard, A. (2023). Is sustainable certification’s ability to combat greenwashing trustworthy? Frontiers in Sustainability, 4, Article 1188069. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2023.1188069
- Oppong-Tawiah D, Webster J. Corporate Sustainability Communication as ‘Fake News’: Firms’ Greenwashing on Twitter. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):6683. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/15/8/6683
- Pabon, J. (2024). The great greenwashing: How brands, governments, and influencers are lying to you. Anansi International. https://www.vitalsource.com/products/the-great-greenwashing-john-pabon-v9781487012878
- Podnar, K., & Golob, U. (2024). Brands and activism: Ecosystem and paradoxes. Journal of Brand Management, 31, 95–107. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41262-024-00355-y
- Rainforest Action Network. (2019). Fifteen environmental NGOs demand that sustainable palm oil watchdog does its job. RAN. https://www.ran.org/press-releases/fifteen-environmental-ngos-demand-that-sustainable-palm-oil-watchdog-does-its-job/
- Renner, A., Zellweger, C., & Skinner, B. (2021). ‘Is there such a thing as sustainable palm oil? Satellite images show protected rainforest on fire’. Neue Zürcher Zeitung. https://www.nzz.ch/english/palm-oil-boom-threatens-protected-rainforest-in-indonesia-ld.1625490
- Saager, E. S., Iwamura, T., Jucker, T., & Murray, K. A. (2023). Deforestation for oil palm increases microclimate suitability for the development of the disease vector Aedes albopictus. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 9514. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-35452-6
- Southey, F. (2021). What do Millennials think of palm oil? Nestlé investigates. Food Navigator. https://www.foodnavigator.com/Article/2021/08/12/What-do-Millennials-think-of-palm-oil-Nestle-investigates
- Transparency International. (2023). Transparency international report: Corruption and corporate capture in Indonesia’s top 50 palm oil companies. Transparency International. https://palmoildetectives.com/2023/05/14/transparency-international-report-corruption-and-corporate-capture-in-indonesias-top-50-palm-oil-companies/
- Truth in Advertising. (2022). Companies accused of greenwashing. https://truthinadvertising.org/articles/companies-accused-greenwashing/
- Truth in Advertising. (n.d.). How causewashing deceives consumers. https://truthinadvertising.org/resource/how-causewashing-deceives-consumers/
- Tybout, A. M., & Calkins, T. (Eds.). (2019). Kellogg on Branding in a Hyper-Connected World. Kellogg School of Management, Northwestern University. https://www.wiley.com/en-au/Kellogg+on+Branding+in+a+Hyper-Connected+World-p-9781119533184
- Wicke, J. (2019). Sustainable palm oil or certified dispossession? NGOs within scalar struggles over the RSPO private governance standard. Bioeconomy & Inequalities: Working Paper No. 8. https://www.bioinequalities.uni-jena.de/sozbemedia/WorkingPaper8.pdf
- World Health Organisation. (2019). The palm oil industry and noncommunicable diseases. World Health Organisation Bulletin, 97, 118-128. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30728618/
- World Rainforest Movement. (2021, November 22). Why the RSPO facilitates land grabs for palm oil. https://wrm.org.uy/articles-from-the-wrm-bulletin/section1/why-the-rspo-facilitates-land-grabs-for-palm-oil/
- Zuckerman, J. (2021). The Time Has Come to Rein In the Global Scourge of Palm Oil. Yale Environment 360, Yale School of Environment. https://e360.yale.edu/features/the-time-has-come-to-rein-in-the-global-scourge-of-palm-oil
Discover more from Palm Oil Detectives
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.










One thought on “Greenwashing Tactic #2: No Proof”