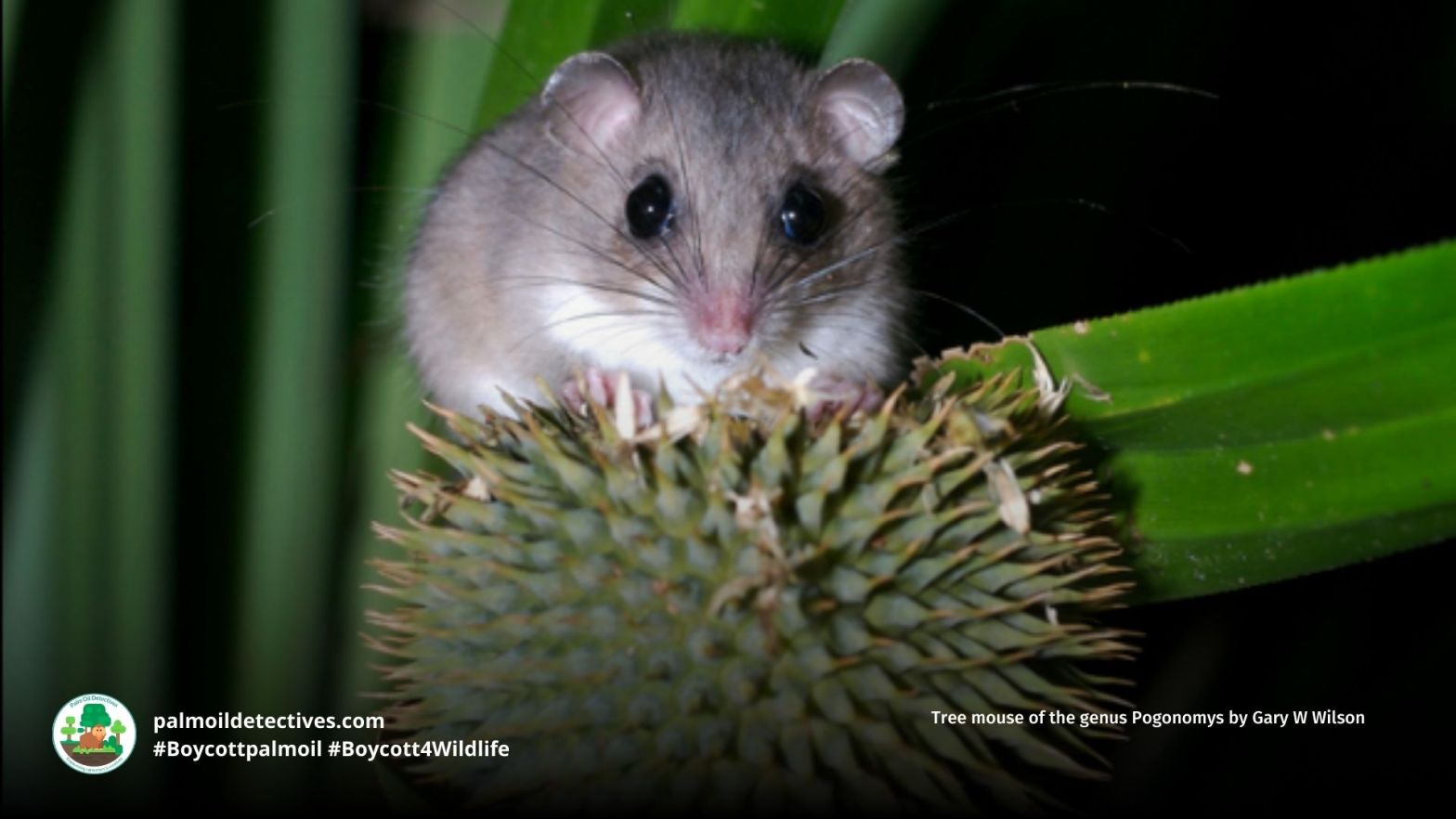
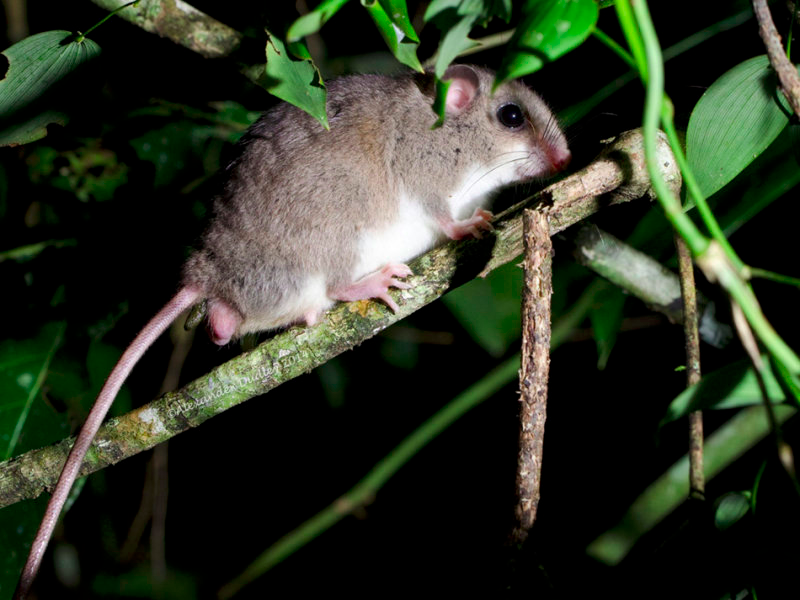
D’entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys Pogonomys fergussoniensis
IUCN Red List Status: Endangered
Location: Papua New Guinea’s D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago.
The D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys has possibly one of the most unpronounceable names in the world and is also one of the least known rodents in the world. also known as the Fergusson Island tree mouse, is an arboreal rodent endemic to Fergusson Island in Papua New Guinea’s D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago. This small, nocturnal rodent species depends on intact montane forests, making them highly vulnerable to habitat destruction caused by out-of-control palm oil plantations, logging, and agricultural expansion. Urgent conservation action is needed to protect this precious and obscure mouse species from extinction. #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife
This diminutive and cute tree #rat 🩷🐀🌳has a difficult name: D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys. They’re #endangered in #PapuaNewGuinea due to #palmoil and #timber #deforestation. Help them survive and #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife @palmoildetect https://palmoildetectives.com/2021/01/31/dentrecasteaux-archipelago-pogonomys-pogonomys-fergussoniensis/
Appearance and Behaviour
The D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys is a small, tree-dwelling rodent with soft, dense fur that ranges from brown to reddish-brown, helping them blend into their forest environment. Their underparts are lighter in colour, and their prehensile tail is a critical adaptation for climbing and balancing in the canopy (IUCN, 2016).
Nocturnal and arboreal, these rodents are elusive and rarely observed. They spend their time foraging in the treetops, relying on their agility to navigate their forested habitat (iNaturalist, n.d.; IUCN, 2016).







Diet
This species primarily consumes fruits, seeds, and plant material, relying heavily on the biodiversity of montane forests. Their specialised diet ties them directly to the health of their ecosystem, and habitat degradation poses a significant threat to their food sources (IUCN, 2016; iNaturalist, n.d.).
Reproduction and Mating
There is limited information about the reproduction of the D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys. Like other species in the Pogonomys genus, they are likely to have small litters. Understanding their reproductive patterns is critical for developing effective conservation strategies (IUCN, 2016).
Geographic Range
This species is restricted to Fergusson Island in Papua New Guinea, where they inhabit montane forests between 1,200 and 1,800 metres above sea level. Their extremely limited range makes them particularly vulnerable to habitat loss for palm oil, timber and gold mining (IUCN, 2016).
Threats

Forest clearance is a serious problem for this species. The islands are being converted to grassland (perhaps entirely) through subsistence farming. This species is assessed as Endangered because of their extent of occurrence (EOO) is approximately 4,922 km², all individuals occur in fewer than six locations, there is continuing decline in the extent and quality of its habitat through deforestation, and the population size is presumed to be decreasing as a result of habitat loss. The species does appear to be tolerant of some disturbance, but this needs to be confirmed.
IUcN Red LIST
Palm oil and timber logging: Deforestation for out-of-control palm oil plantations, agriculture, and timber logging is destroying their montane forest habitat at an alarming rate (IUCN, 2016).
Climate Change: Rising temperatures could further reduce the availability of suitable montane habitats, forcing these small tree-dwelling rodents into even smaller ranges.
Conservation Neglect: As a lesser-known species, they receive minimal attention in conservation efforts, further jeopardising their survival.
Take Action!
Safeguarding the D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys requires immediate action to preserve their fragile forest habitat. Boycotting products containing palm oil, supporting indigenous-led conservation, and advocating for biodiversity protection are essential steps to ensure their survival. Every effort matters. #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife #Vegan
Further Information
Wright, D & Leary, T. 2016. Pogonomys fergussoniensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T136763A22431006. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136763A22431006.en. Downloaded on 31 January 2021.
iNaturalist. (n.d.). Pogonomys fergussoniensis. Retrieved from https://uk.inaturalist.org/taxa/74934-Pogonomys-fergussoniensis
Wikipedia. (n.d.). D’Entrecasteaux Archipelago Pogonomys. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D%27Entrecasteaux_Archipelago_pogonomys
Support the conservation of this species

How can I help the #Boycott4Wildlife?
Take Action in Five Ways
1. Join the #Boycott4Wildlife on social media and subscribe to stay in the loop: Share posts from this website to your own network on Twitter, Mastadon, Instagram, Facebook and Youtube using the hashtags #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife.
2. Contribute stories: Academics, conservationists, scientists, indigenous rights advocates and animal rights advocates working to expose the corruption of the palm oil industry or to save animals can contribute stories to the website.
3. Supermarket sleuthing: Next time you’re in the supermarket, take photos of products containing palm oil. Share these to social media along with the hashtags to call out the greenwashing and ecocide of the brands who use palm oil. You can also take photos of palm oil free products and congratulate brands when they go palm oil free.
4. Take to the streets: Get in touch with Palm Oil Detectives to find out more.
5. Donate: Make a one-off or monthly donation to Palm Oil Detectives as a way of saying thank you and to help pay for ongoing running costs of the website and social media campaigns. Donate here
Discover more from Palm Oil Detectives
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.








