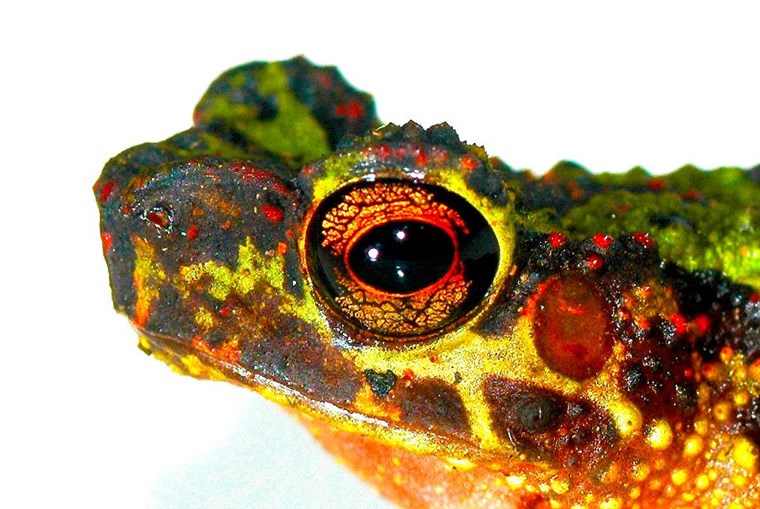
Bornean Rainbow Toad Ansonia latidisca
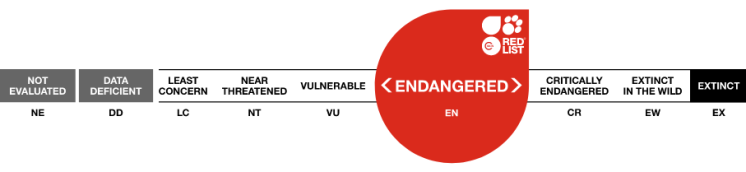
Endangered
Indonesia (Kalimantan); Malaysia (Sarawak)
The Bornean Rainbow Toad, also known as the Sambas Stream Toad, is a vibrantly coloured amphibian native to the rainforests of Borneo. This elusive species was rediscovered in 2011 after being unseen since 1924. Endemic to the montane rainforests, these amphibians are nocturnal and arboreal, with long, spindly limbs and a bright, variegated dorsal skin. Their striking appearance and nocturnal habits make them a unique sight in their natural habitat. The primary threats to their survival include habitat loss due to deforestation for agriculture, particularly palm oil plantations. Protecting their habitat is crucial for their survival. Join the cause to #Boycottpalmoil and #Boycott4Wildlife.
The Bornean Rainbow #Toad is a vibrant array of beautiful colours 🌈 Endangered by #palmoil #deforestation in #Indonesia #Malaysia. Save this handsome amphibian 🐸 and forgotten animal when u #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife @palmoildetect https://palmoildetectives.com/2021/01/25/bornean-rainbow-toad-ansonia-latidisca
Meet the Bornean Rainbow #Toad! 🌈🐸 This vivid #amphibian is #endangered and faces serious threats from #palmoil #deforestation in #Borneo. Help them every time you shop 🛒🛍️ and #Boycottpalmoil 🪔🚫#Boycott4Wildlife in the supermarket @palmoildetect https://palmoildetectives.com/2021/01/25/bornean-rainbow-toad-ansonia-latidisca
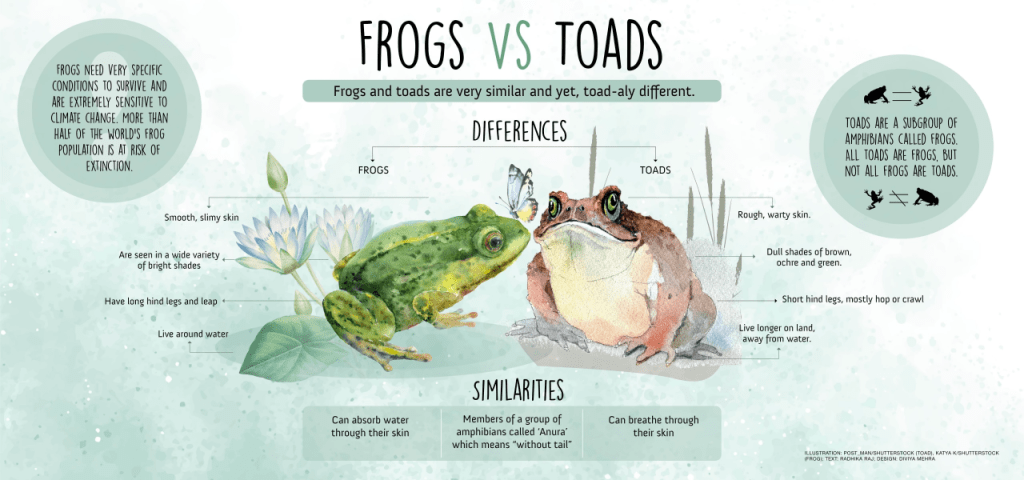
Appearance
The Bornean Rainbow Toad is a small species, measuring between 30 to 50 mm in length. They possess bright green, purple, and red variegated dorsal skin with a pebbly texture, which indicates possible poison glands. Their long, spindly limbs are well-adapted for climbing, and their vibrant colours provide excellent camouflage against the mossy tree bark of their rainforest habitat. These unique adaptations not only help them evade predators but also make them a fascinating subject for researchers and conservationists.
Mating and Breeding
Little is known about the specific mating habits of the Bornean Rainbow Toad, but they are likely similar to other frogs and members of their genus. Males may call to attract females during the breeding season, and eggs are probably deposited in streams. The species is believed to have torrent-adapted tadpoles, which develop in fast-flowing water. Understanding their reproductive behaviour is essential for conservation efforts, as it can help in creating effective breeding programs to boost their population in the wild.
Diet
As nocturnal foragers, the Bornean Rainbow Toad primarily feeds on small insects and invertebrates. They hunt at night, using their keen vision and agility to capture prey. Their diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem, as they help control insect populations. The availability of food sources is directly linked to the health of their habitat, making the preservation of their rainforest environment vital for their survival.
Threats
These tiny and vividly coloured frogs are endangered due to a multitude of human-related causes:
The main threat to this species of toad is habitat loss and degradation primarily as a result of logging.
IUCN red list
- Deforestation and habitat loss: for agriculture, timber and palm oil plantations
- Logging and land conversion: for recreational use and infrastructure projects.
- Pollution run-off: from logging and agricultural activities.
- Poaching and illegal capture: for the international pet trade.
The Bornean Rainbow Toad faces significant threats from habitat destruction and degradation. Deforestation for palm oil plantations is a major concern, as it leads to the loss of their natural habitat and food sources. Logging activities not only destroy their habitat but also cause sedimentation of streams, which impacts their breeding grounds. Poaching for the international pet trade adds to the pressure on their population. To protect these unique amphibians, it is essential to address these threats and promote sustainable practices.
The importance of conserving their rainforest home
Effective preservation of the hilly rainforest regions in Borneo is crucial for the survival of the Bornean Rainbow Toad. Conservation efforts should focus on protecting their natural habitat from deforestation and degradation and supporting indigenous sovereignty.
Join the movement to #Boycottpalmoil and #Boycott4Wildlife, and help safeguard the future of the Bornean Rainbow Toad.
Further Information
IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group. 2018. Ansonia latidisca. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T54471A114916284. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T54471A114916284.en. Downloaded on 25 January 2021.
Wikipedia contributors. (2024). Ansonia latidisca. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved from Wikipedia
Animalia.bio. (2024). Bornean Rainbow Toad. Retrieved from Animalia.bio
FAQS on Bornean Rainbow Toads
1. Are Bornean Rainbow Toads poisonous?
Bornean Rainbow Toads may possibly be poisonous. They possess bright green, purple, and red variegated dorsal skin with a pebbly texture, indicating possible poison glands.
2. What are the adaptations of Bornean Rainbow Toads?
Bornean Rainbow Toads have several adaptations, including their bright, multicoloured skin that serves as camouflage in their natural rainforest habitat. Their long limbs help them navigate the dense, arboreal environment.
3. What biome do Bornean Rainbow Toads inhabit?
Bornean Rainbow Toads are found in the rainforest biome of Borneo, specifically in the montane regions where they reside on trees and vegetation.
4. What do Bornean Rainbow Toads eat?
The diet of Bornean Rainbow Toads primarily consists of small insects and invertebrates, which they hunt in the forest underbrush and on tree trunks.
5. What is the behaviour of Bornean Rainbow Toads?
Bornean Rainbow Toads are nocturnal creatures, most active at night. They are known for their elusive nature and tendency to remain hidden in the dense foliage of their habitat.
6. How much do Bornean Rainbow Toads weigh?
Bornean Rainbow Toads are a small species, typically weighing around 20 to 30 grams.
7. What is the habitat of Bornean Rainbow Toads?
Bornean Rainbow Toads inhabit the montane rainforests of Borneo, often found at elevations between 900 and 1,700 meters. They prefer moist, shaded environments with plenty of foliage for cover.

How can I help the #Boycott4Wildlife?
Take Action in Five Ways
1. Join the #Boycott4Wildlife on social media and subscribe to stay in the loop: Share posts from this website to your own network on Twitter, Mastadon, Instagram, Facebook and Youtube using the hashtags #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife.
2. Contribute stories: Academics, conservationists, scientists, indigenous rights advocates and animal rights advocates working to expose the corruption of the palm oil industry or to save animals can contribute stories to the website.
3. Supermarket sleuthing: Next time you’re in the supermarket, take photos of products containing palm oil. Share these to social media along with the hashtags to call out the greenwashing and ecocide of the brands who use palm oil. You can also take photos of palm oil free products and congratulate brands when they go palm oil free.
4. Take to the streets: Get in touch with Palm Oil Detectives to find out more.
5. Donate: Make a one-off or monthly donation to Palm Oil Detectives as a way of saying thank you and to help pay for ongoing running costs of the website and social media campaigns. Donate here
Discover more from Palm Oil Detectives
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.








