Pileated Gibbon Hylobates pileatus
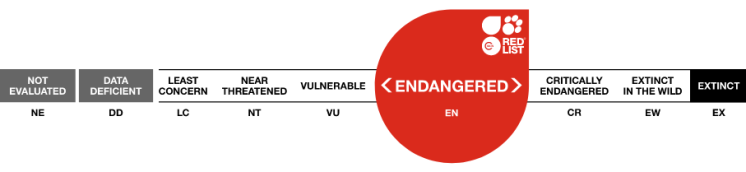
Endangered
Cambodia; Laos, Thailand
The charming pileated #gibbon 🐒 partners for life and sings in a regional “accent”. Don’t let forests go silent! They’re threatened by #hunting and #palmoil #deforestation Take action! 🌴🔥⛔️ #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife https://palmoildetectives.com/2021/02/08/pileated-gibbon-hylobates-pileatus/
Pileated gibbons form close bonds with their partners and children 🐵🐒🙉. They’re endangered in #Laos #Cambodia #Thailand by #hunting and #deforestation for #palmoil and #timber. Fight for them and #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife @palmoildetect https://palmoildetectives.com/2021/02/08/pileated-gibbon-hylobates-pileatus/
The Pileated Gibbon is listed as Endangered as they are suspected to have experienced a reduction of more than 50% over a time frame of three generations (45 years) in the past. Most populations are not yet secured in protected areas, and the main threats are habitat loss due to logging, agricultural conversion, hydroelectric development and new human settlements (W. Brockelman pers. Comm.)
IUCN Red List
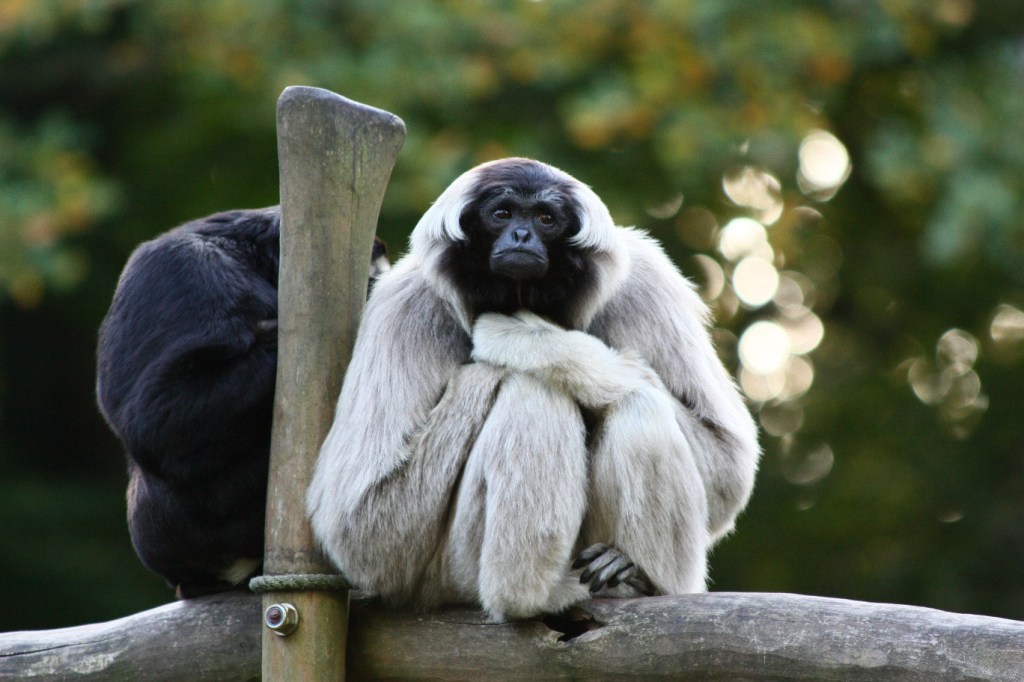





Appearance and Behaviour
The Pileated Gibbon belongs to the genus Hylobates. The word Hylobates means ‘Forest Walker’ in Greek. The gibbons in this genus are known for the white circle of fur around their faces. They are known to communicate in species-specific song when defining territory or attracting mates. They sing in regional accents to each other, have long swinging arms, inquisitive natures and superior acrobatic skills, they spend most of their lives high up in the tree-tops. Researchers find the species somewhat shyer and more elusive than the Lar Gibbon (W. Brockelman pers. Comm.)
Mating and Reproduction
The Pileated Gibbons form strong monogomous bonds with their partners and children.
Habitat and Geographic Range
They live in moist, seasonal evergreen and mixed deciduous-evergreen forests and have been recorded living to about 1,500 m in Cambodia and to around 1,200 m in Thailand.
Diet
The Pileated Gibbon is similar to the Lar Gibbon in diet and general ecology and they eat mostly fruits, shoots, and some immature leaves, as well as insects (Srikosamatara 1980, 1984).
Threats
Hunting and habitat loss: This species is threatened by both hunting, primarily for subsistence, and severe habitat fragmentation and degradation (Duckworth et al. 1999, Traeholt et al. 2005).
In Thailand, all populations are now within protected conservation areas and the era of logging and slash-and-burn agriculture (Brockelman 1983) is now mostly over.
Deforestation even in ‘protected’ forests is a threat: Nevertheless, severe encroachment has occurred in eastern Khao Yai Park and other major protected areas, and subsistence hunting by minor forest product collectors is still uncontrolled (Phoonjampa and Brockelman 2008). In Cambodia, however, habitat destruction is a more immediate threat than poaching, especially in remote areas.
Most populations are not yet secured in protected areas, and the main threats are habitat loss due to logging, agricultural conversion, hydroelectric development and new human settlements (W. Brockelman pers. Comm.)

Support the conservation of this species
This animal has no protections in place. Read about other forgotten species here. Create art to support this forgotten animal or raise awareness about them by sharing this post and using the #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife hashtags on social media. Also you can boycott palm oil in the supermarket.
Further Information
Brockelman, W, Geissmann, T., Timmins, T. & Traeholt, C. 2020. Hylobates pileatus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T10552A17966665. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T10552A17966665.en. Downloaded on 08 February 2021.

How can I help the #Boycott4Wildlife?
Take Action in Five Ways
1. Join the #Boycott4Wildlife on social media and subscribe to stay in the loop: Share posts from this website to your own network on Twitter, Mastadon, Instagram, Facebook and Youtube using the hashtags #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife.
2. Contribute stories: Academics, conservationists, scientists, indigenous rights advocates and animal rights advocates working to expose the corruption of the palm oil industry or to save animals can contribute stories to the website.
3. Supermarket sleuthing: Next time you’re in the supermarket, take photos of products containing palm oil. Share these to social media along with the hashtags to call out the greenwashing and ecocide of the brands who use palm oil. You can also take photos of palm oil free products and congratulate brands when they go palm oil free.
4. Take to the streets: Get in touch with Palm Oil Detectives to find out more.
5. Donate: Make a one-off or monthly donation to Palm Oil Detectives as a way of saying thank you and to help pay for ongoing running costs of the website and social media campaigns. Donate here
Discover more from Palm Oil Detectives
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.









One thought on “Pileated Gibbon Hylobates pileatus”