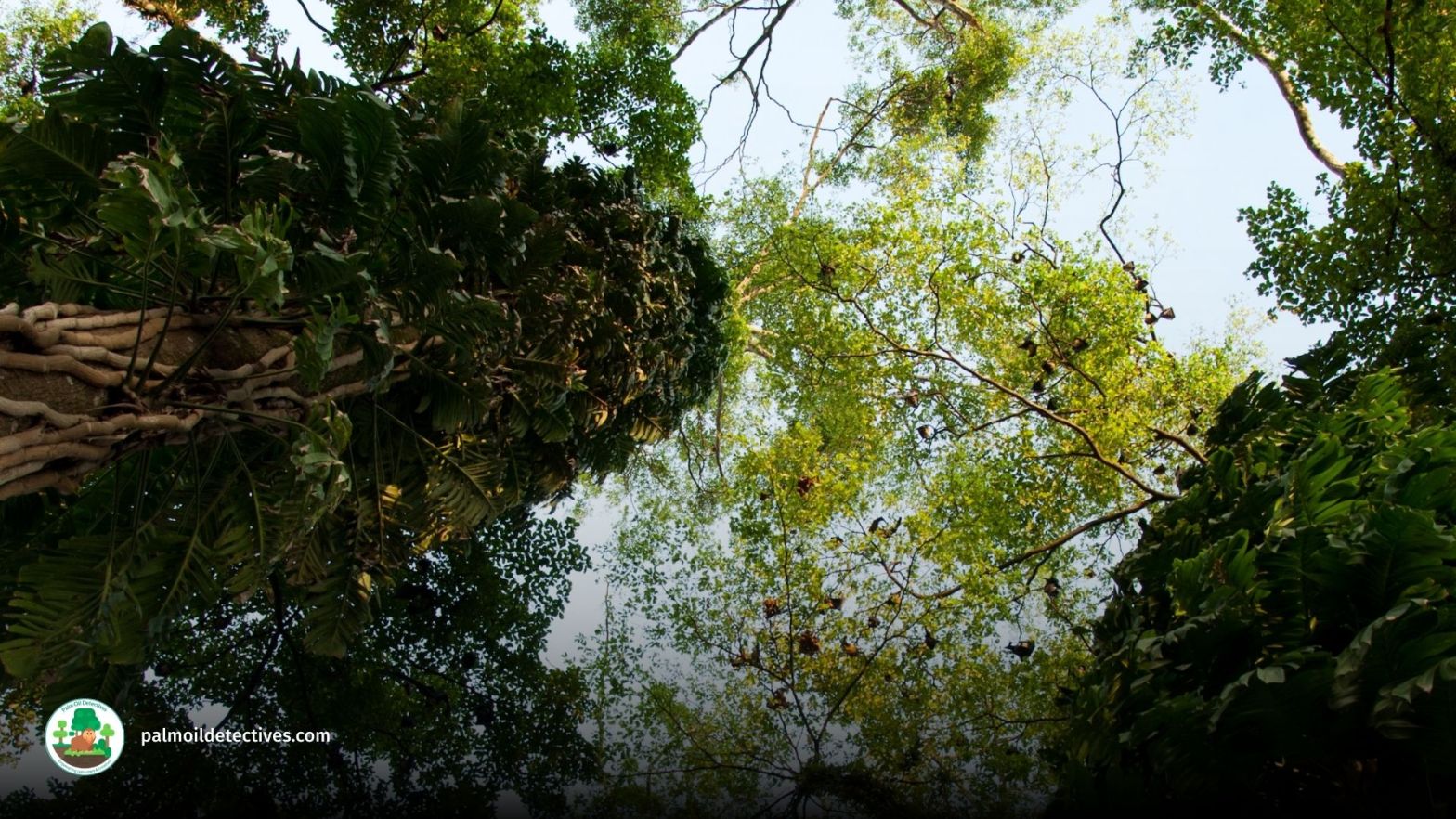
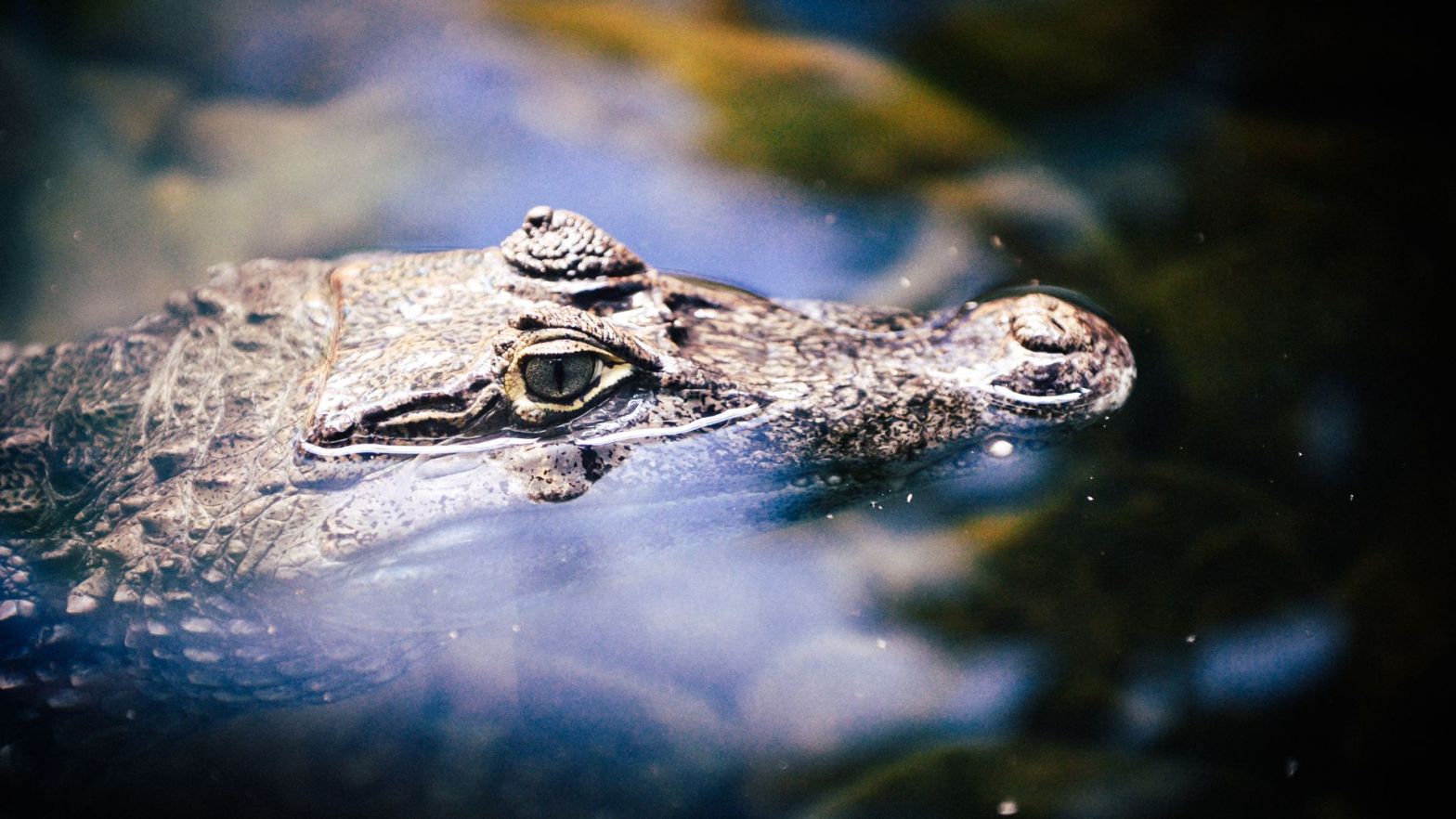
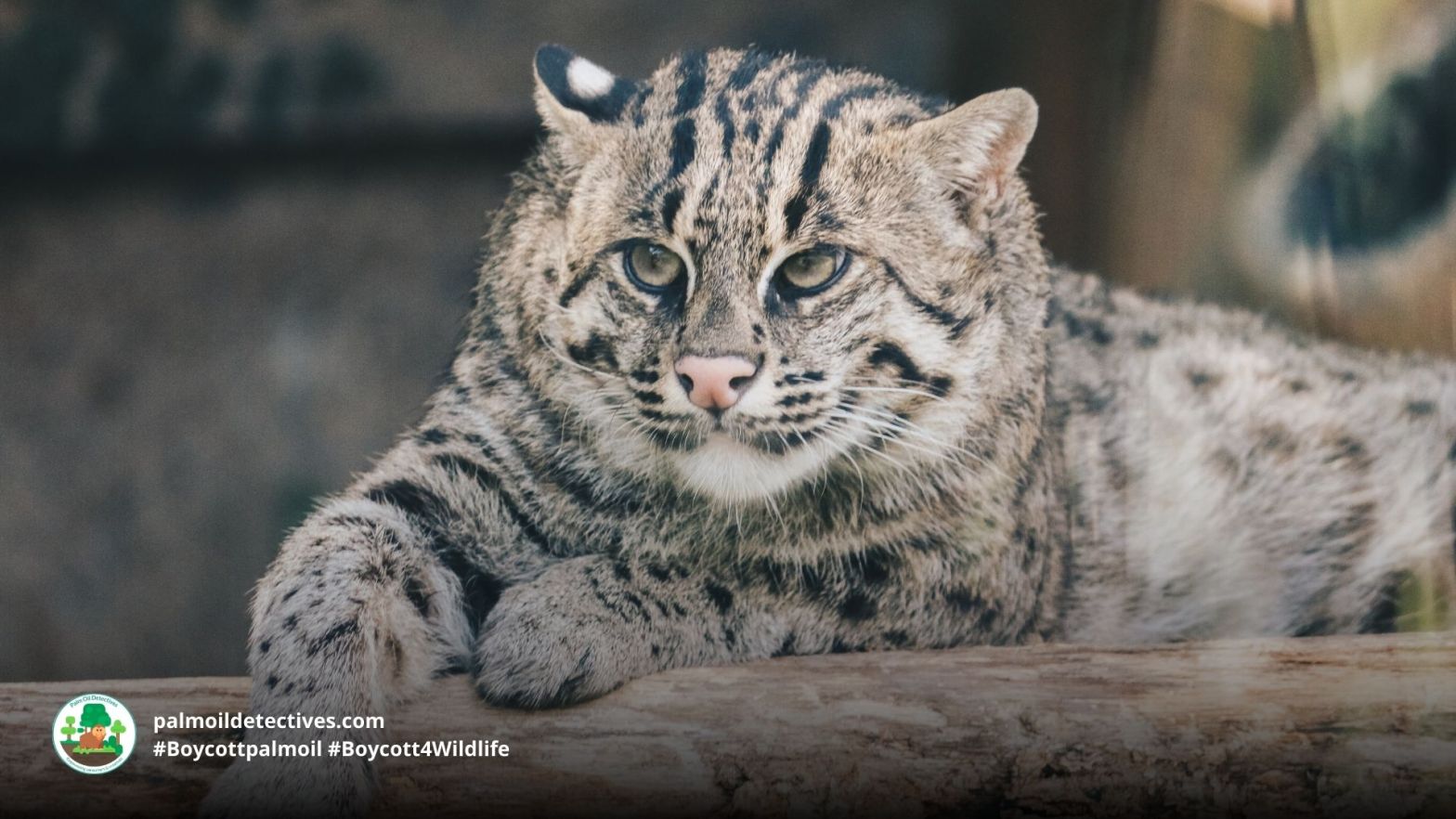
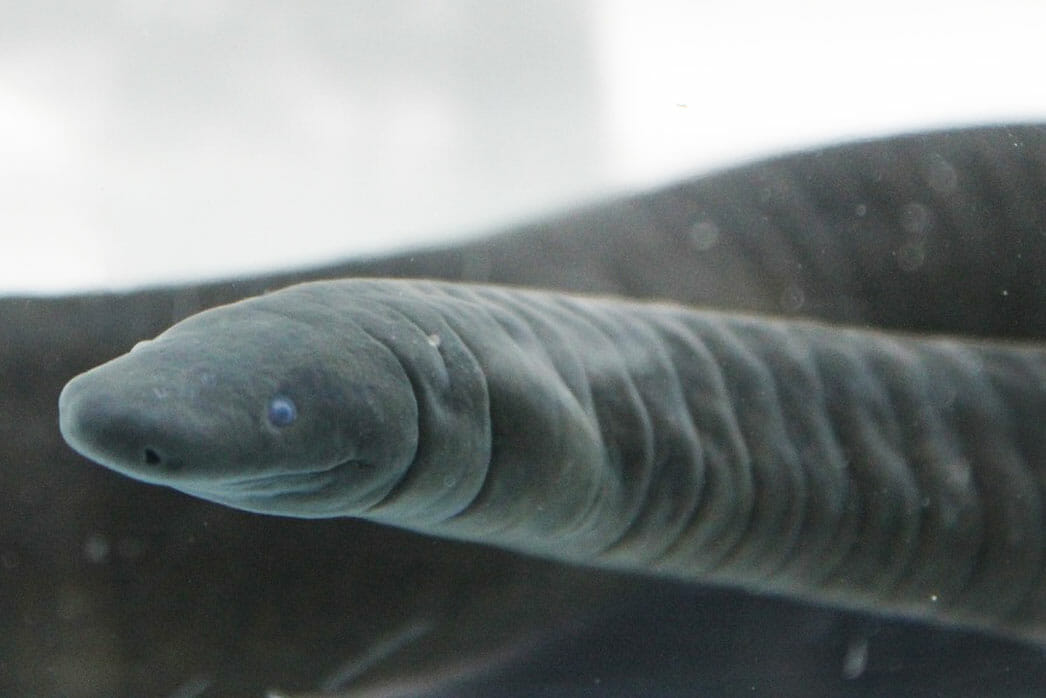
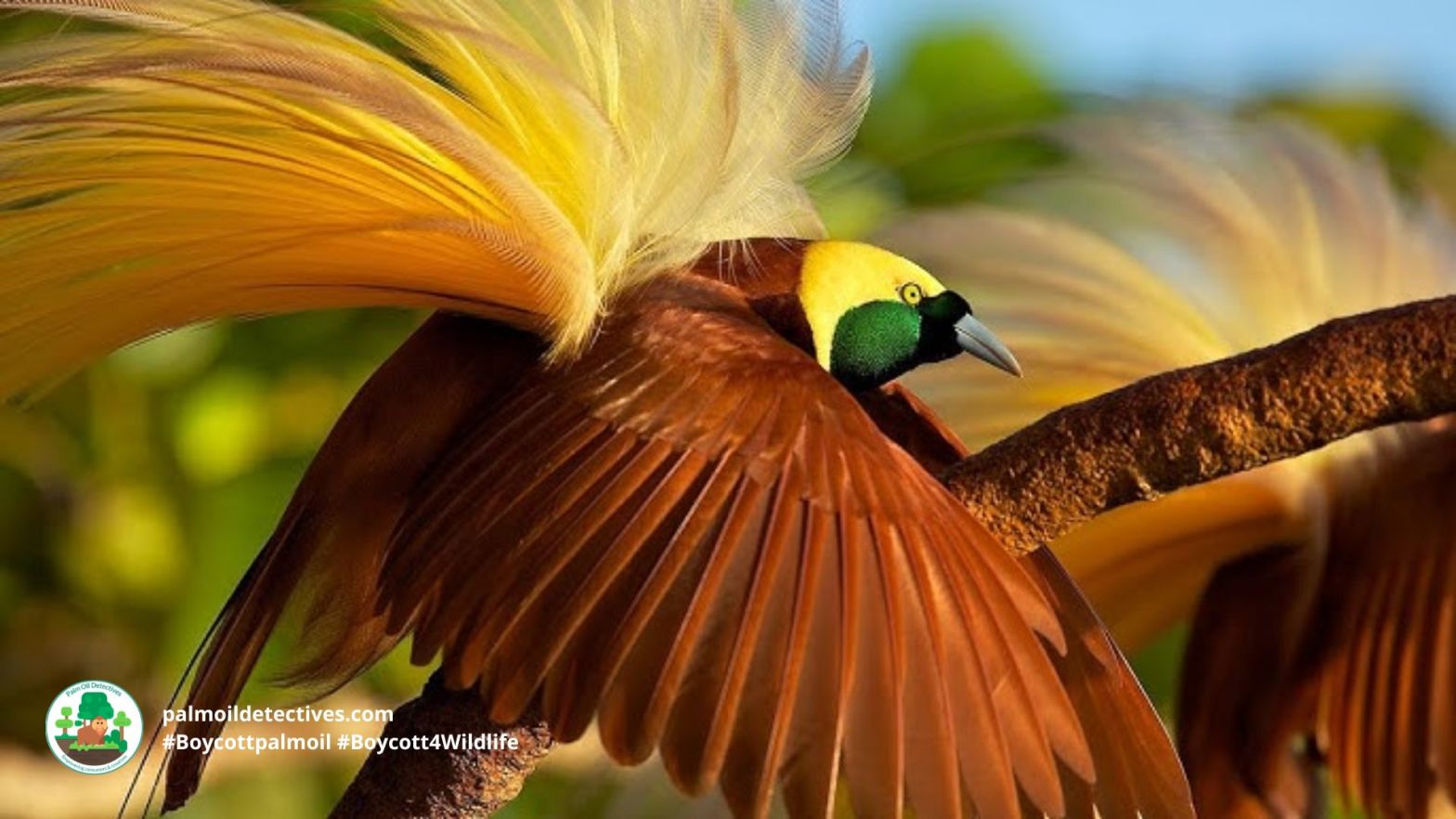
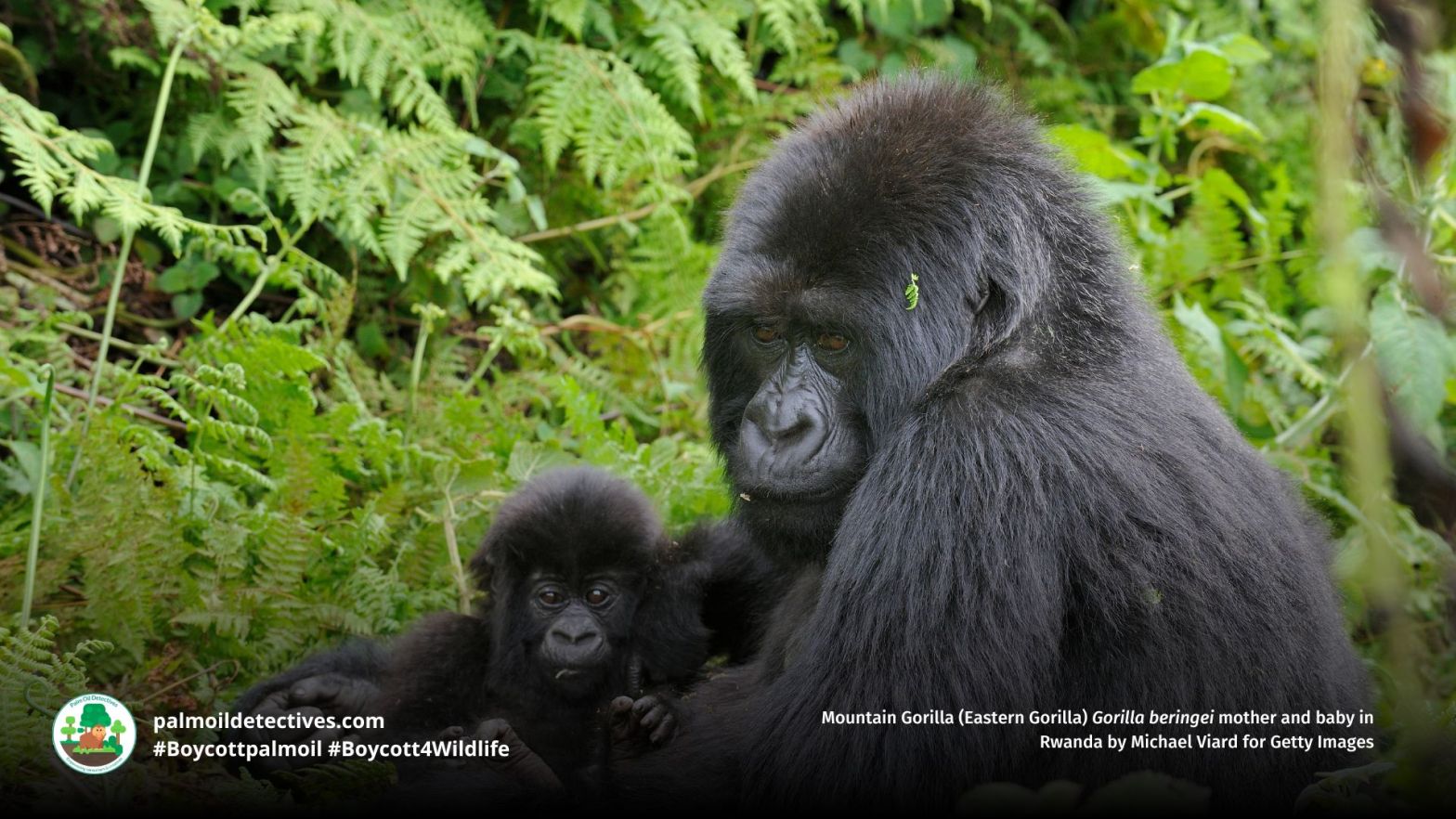
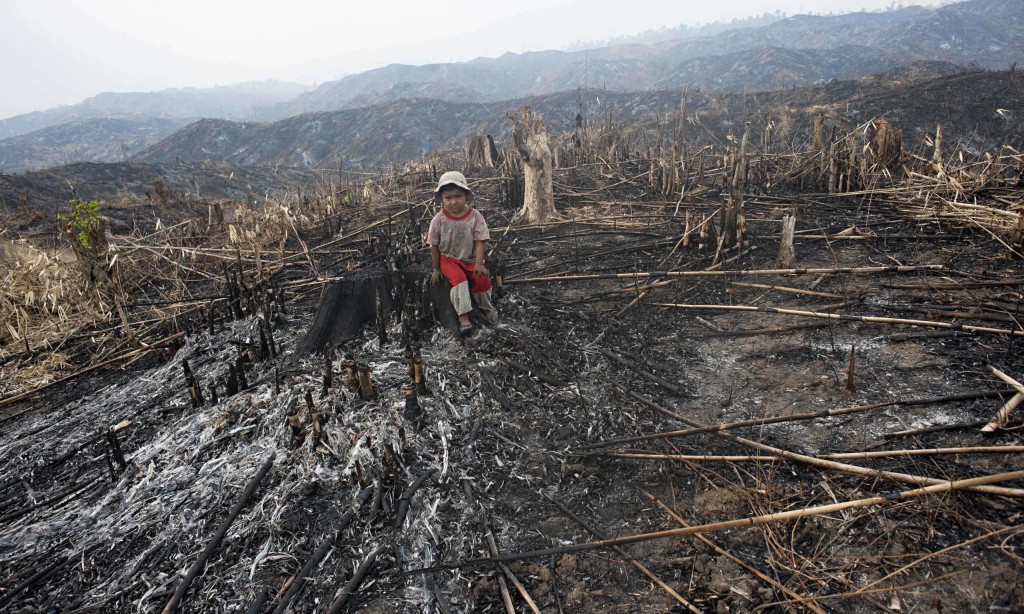
A recent study using satellite data has highlighted the critical role that large herbivores play in promoting tree diversity in forest ecosystems. The research showed that areas with abundant large herbivores had more varied tree cover and more tree diversity. This finding underscores the importance of large herbivores in many ecosystems and that they should have primary importance in conservation strategies, particularly in the context of global efforts to combat climate change and extinction. Help big herbivores every time you shop and #Boycottpalmoil and #Boycott4Wildlife in the supermarket!
Tag Archives: biodiversity
Seven practical ways to stop a species wipeout
1 million #plants 🌾🌽🎍🍅 and #animals 🦏🦒🐅 are threatened. #Wildlife and #biodiversity are at a crossroads of #extinction. Here’s 7 practical ways to stop #species wipeout. Help them survive! #Boycottpalmoil 🌴☠️🚫 #Boycott4Wildlife
Phayre’s Leaf Monkey Trachypithecus phayrei
Phayre’s leaf monkey, also known as Phayre’s langur, are remarkable Old World monkeys distinguished by large, white-rimmed eyes that lend them a “spectacled” appearance. Known locally as ‘Chasma bandor’ they live mostly in the lush forests of India, Bangladesh and Myanmar. Major threats to their survival include habitat destruction from palm oil and rubber plantations, illegal hunting for traditional medicine, and habitat encroachment depleting their natural food sources. An emerging threat is interbreeding with other threatened monkey species. Join the fight to protect this unique species: #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife in the supermarket! If you care about animals, consider going #Vegan to protect their habitat and lives.
Protected: Private Advocate’s Page
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Amazon Clarion Call: Pandemics Emerging in the Rainforest
The Amazon’s diverse ecosystem is under threat from rampant deforestation, degradation, a biodiversity crisis, and the climate crisis – jeopardising its ability to act as a carbon sink. This degradation increases the likelihood of zoonotic diseases emerging and spreading, posing a significant public health risk for Brazil and the world. #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife
Deforestation comes ‘roaring back’ despite 140-country vow to end destruction
A new report has found that demand for #meat, #soy, #palmoil and nickel #mining is hindering efforts to halt #deforestation by 2030, a global report finds. The destruction of global forests increased in 2023, and is higher than when 140 countries promised three years ago to halt deforestation by the end of the decade.
The rising destruction of the forests puts ambitions to halt #climatechange and stem the huge worldwide #extinction even further from reach, the researchers warn. They found that voluntary certification of commodities alone could not stop deforestation and that strong legislation was needed to stop the ecocide and destruction.
How does Indonesia’s palm oil industry fuel the climate crisis?
Booming global demand for the vegetable oil is spurring deforestation in Indonesia. Indonesia accounts for more than half of the global palm oil supply, the world’s most widely used vegetable oil that is found in everything from food to cosmetics to fuel.
But environmentalists fear surging demand for the product may drive mass deforestation in Indonesia, home to the world’s third-largest tropical rainforest, and exacerbate the global climate crisis.
Protect Nature to Avoid Future Pandemics
Research from University of Queensland and published in The Lancet: Planetary Health finds that the COVID-19 pandemic is linked to the decline of ecosystems and biodiversity, creating a cycle that could lead to more pandemics. The pandemic, caused by a virus jumping from animals to humans, has worsened deforestation, increasing human-wildlife contact and the risk of future disease outbreaks. The study emphasizes the need for a One Health approach, combining public health, conservation efforts and involving indigenous custodianship of land and indigenous traditional knowledge to prevent outbreaks by protecting ecosystems. We must safeguard biodiversity to prevent more pandemics. #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife
Bird species are facing extinction hundreds of times faster than previously thought
Extinction, or the disappearance of an entire species, is commonplace. Yet evidence suggests that the number of bird species going extinct, and the rate at which they are disappearing, is increasing dramatically. Conserving species at the 11th hour is difficult and expensive, the key is definitely prevention. To go hard and go early and stop species disappearing. Help rainforest animals on the verge of extinction from deforestation by changing your shopping habits. #Boycottmeat #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife
Amphibians Glow in Ways People Can’t See
Many animals have a colourful, yet largely hidden, trait. Marine creatures like #fish and corals can glow blue, green or red under certain types of light. So can land animals like penguins and #parrots. But until now, experts knew of only one salamander and a few #frogs that could glow. No longer. Among #amphibians, this ability to glow now appears fairly common — even if you can’t see it. Research has found that most amphibians glow as well – even if it’s not visible to human eyes. Protect amphibians and reptiles every time you shop and #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife
Extinction On Our Plates
The contents of your fridge and dining table directly impacts the future of rare rainforest and ocean animals. That’s because industrial agriculture and aquaculture for commodities like meat, dairy, fish and palm oil is driving animals in the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet closer towards extinction.
However, reducing the biodiversity footprint of global food consumption requires more than just consumer intervention. It requires immediate and widespread action from government policy-makers and law-makers as well, writes Ecologist Dr Quentin Read of North Carolina State University for 360info
African Forest Elephants Help Fight Climate Change
Discover the awe-inspiring role of African forest elephants in the Congo Basin—nature’s master gardeners who literally shape the world around them! These gentle giants roam through muddy, mineral-rich paradises called baïs, fostering the growth of carbon-absorbing trees that make our planet healthier. By tending to these unique landscapes, they are the unsung heroes in the fight against climate change. Want to ensure these ecological architects keep doing their vital work? Join the movement to protect their habitat—say no to palm oil and adopt a vegan lifestyle! 🐘🌳#BoycottPalmOil #BeVegan #Boycott4Wildlife
Strange Species Could Vanish Before Discovery
Scientists have described around 1.5 million species on Earth – but how many are still out there to be discovered? This is one of the most heated debates in biology. Discounting microbes, plausible estimates range from about half a million to more than 50 million species of unknown animals, plants and fungi.
Our present knowledge is just scratching the surface. Evolution has had billions of years to create biologically active compounds that can combat human diseases, generate genetic diversity that could save our food crops from disastrous pathogens, and spawn ecological innovations that can inspire marvellous new inventions. Help the rarest and most cryptic animals, plants and fungi to survive when you #BoycottPalmOil adopt a #vegan lifestyle and #Boycott4Wildlife
Palm Oil Increases Deaths of Baby Macaques
In Peninsular Malaysia, a new study published in Cell Biology by a team led by Dr Anna Holzner of German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) Halle-Jena-Leipzig has found that infant mortality rates among wild southern pig-tailed macaques are alarmingly high due to frequent visits to oil palm plantations.
These plantations expose the infants to increased risks from predators, human encounters, and harmful agricultural chemicals, potentially affecting the development and survival of infant macaques. The study, conducted in collaboration of international researchers, observed that prolonged exposure to these plantations during infancy triples the likelihood of death.
The study suggests that pesticides used in agriculture could cross the placental barrier or be transmitted through breastmilk, impacting fetal development and health. This significant research underlines the urgent need for eco-friendly agricultural practices to protect wildlife and human communities near plantations. Take action and join the movement to #Boycottpalmoil and #Boycott4Wildlife every time you shop!
Rethinking Climate and Extinction Crises
Capturing people’s attention about the #climate and #extinction crises is a challenge. Causes mostly move slowly, without the flashy drama that can focus our minds in the midst of 24-hour news cycles and social media distractions. The Netflix film Don’t Look Up cleverly captures humans’ inability to come together to counter such a common existential threat. To change this, we must develop a “slow memory” that can help us care about and act on slow change. Help to fight against extinction when you shop and #Boycottpalmoil #Boycott4Wildlife
Choose Indigenous Trees Over Palm Oil In India
India is pushng palm oil growth, a massive mistake for local biodiversity, land rights and climate change, Indians should resist and Boycott palm oil!
300,000 Trees Tracked: Are Losing Their Power to Help Us
Tropical forests matter to each and every one of us. They suck colossal quantities of carbon out of the atmosphere, providing a crucial brake on the rate of climate change. Yet a statistical model in this study has estimated that by 2030 the African forests’ capacity to remove carbon will decrease by 14%, while Amazonian forests may stop removing carbon dioxide altogether by 2035. What can you do? Use our wallet as a weapon and #Boycottpalmoil #Boycottmeat #Boycott4Wildlife
Caring for Siamese crocodiles in Cambodia
Researchers travel into the remote wilderness of #Cambodia to study the world’s most endangered #crocodile, the placid, cryptic and little-known Siamese crocodile. Help their survival in the supermarket and be #vegan, boycott crocodile leather and #Boycott4Wildlife
The right for nature to simply exist is clear – the movement to enshrine this into law is growing
The idea that nature — forests , rivers, mountains — could have rights, in the same way that human rights, or corporate rights exist has been building momentum. A historic global agreement has been reached to try to protect the plants and animals of this world from further demise.
Uncovering The Glasswing Butterfly’s See-through Wings
Most butterflies sport colourful, eye-catching wings. But some species flit about using mostly transparent wings. Researchers have now uncovered the tricks that one of these — the glasswing butterfly (Greta oto) — uses to hide in plain sight. The tricks of their transparency include sparse, spindly scales and a waxy coated membrane. Many thousands of insect species are threatened by large-scale deforestation for agriculture and especially pesticides. Help them to survive and #BoycottPesticides #BoycottPalmOil!
Palm Oil: A Recipe for Disaster in India
Given the widespread destruction of rainforests and native biodiversity caused by oil palm plantations in Southeast Asia, environmental experts and politicians are warning that the move to promote palm oil cultivation in India’s northeastern States and in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands could be disastrous, writes Priscilla Jerbaraj in The Hindu.
Thousands more species at risk of extinction than currently recorded, suggests new study
New research suggests the #extinction crisis may be even worse than we thought. More than half of species that have so far evaded any official conservation assessment are threatened with extinction. Some species that are not yet classified and are “data deficient” make up around 17% of the nearly 150,000 species currently assessed. according to predictions by researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Help them to survive! #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife
Caecilians: Secretive Underground Dwellers
OK, Ok…I know this is quite a scary photo but hear me out. Caecilians are legless, eyeless creatures live secretive, strange lives underground and underwater. Not quite snakes, not quite worms and not quite amphibians either.
Once you know more about them they may still come to you in dreams, but you might just love them too.
They belong to the same group of animals that includes frogs and salamanders. But unlike other amphibians, caecilians lack legs. Some caecilians are as short as a pencil, while others grow as long as a child. Their eyes are tiny and hidden beneath skin and sometimes bone. And they have a pair of tentacles on their face that can sniff out chemicals in the environment.
The mimics among us — birds pirate songs for personal profit
From Roman classics to British tabloids, humans have long celebrated the curious and remarkable ability of #birds and other #animals to imitate the sounds of humans and other animals. A recent surge of research is revealing how and why birds use vocal mimicry to further their own interests. Far from being merely a biological curiosity,Continue reading “The mimics among us — birds pirate songs for personal profit”
Almost 90% of the world’s animal species will lose some habitat to agriculture by 2050
Scientists know that #biodiversity is declining across much of the world although less universally and dramatically than we feared. We also know that things are likely to get worse in the future, with a combination of #deforestation, #climatechange and overexploitation set to drive species and habitats ever closer to #extinction. Help them every time you shop and be #vegan #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife
Research: Small room for compromise between oil palm cultivation and primate conservation in Africa
Research shows that future palm oil expansion is a major threat to Africa’s tropical forests and their rich primate biodiversity, Fight back boycott palm oil!
Research: Zoonotic Disease Outbreaks Linked to Forest Cover and Palm Oil Expansion
#Research finds that #deforestation is a major cause of #biodiversity loss with a negative impact on human health. Outbreaks of vector-borne #zoonotic #diseases are associated with increases in areas of #palmoil plantations.
Dayak Indigenous Ethnographer Dr Setia Budhi
Dr Setia Budhi is a senior lecturer in Anthropology and Sociology at Universitas Lambung Mangkurat. He is an indigenous advocate, forest conservationist and a research specialist in Dayak ethnography in South, Central and East Kalimantan. He completed his PhD in 2010 at UKM Malaysia under the supervision of Prof. Awang Hasmadi Awang Moeis and Prof. Aishah Bt Mohamed. He now serves as Head of the Sociology Department and a member of the Indonesian Anthropology Association of South Kalimantan-Indonesia.
His research relates to the Dayak people and impact of socio-cultural changes, exploitation of natural resources and modernisation on their lives. In particular, he investigates how the depletion of the forest affects the availability of food sources for Indigenous Dayak peoples.
Nature’s Hidden Wealth: Conservation’s Opportunity
Animals and plants constitute a very small part of our native biodiversity (roughly 5%). The vast majority – fungi, bacteria and the enormous diversity of other microscopic organisms, including invertebrates – is a massive, largely unexplored economic resource.
The best known examples of commercial uses for biodiversity are the thousands of drugs secreted by bacteria and fungi. But others are examples of what is known as “bio-inspiration” and “bio-mimicry”, where wild species provide the blueprints for products. The combination of nature and biotechnology can offer us all a tentative reason to hope for the future.
Palm oil plantations are bad for wildlife great and small: study
#Palmoil plantations have an overall negative impact on #biodiversity, according to research released this week. The #study, published in Nature Communications, found palm oil plantations are home to fewer insect species than even intensive rubber tree plantations. A forests expert at James Cook University, Bill Laurance, said of the research: “The big message is that oil palm is bad for biodiversity, in every sense of the word — even when compared to damaged rainforests that are regenerating after earlier logging or clearing.” Make sure you take action every time you shop and #BoycottPalmOil #Boycott4Wildlife!